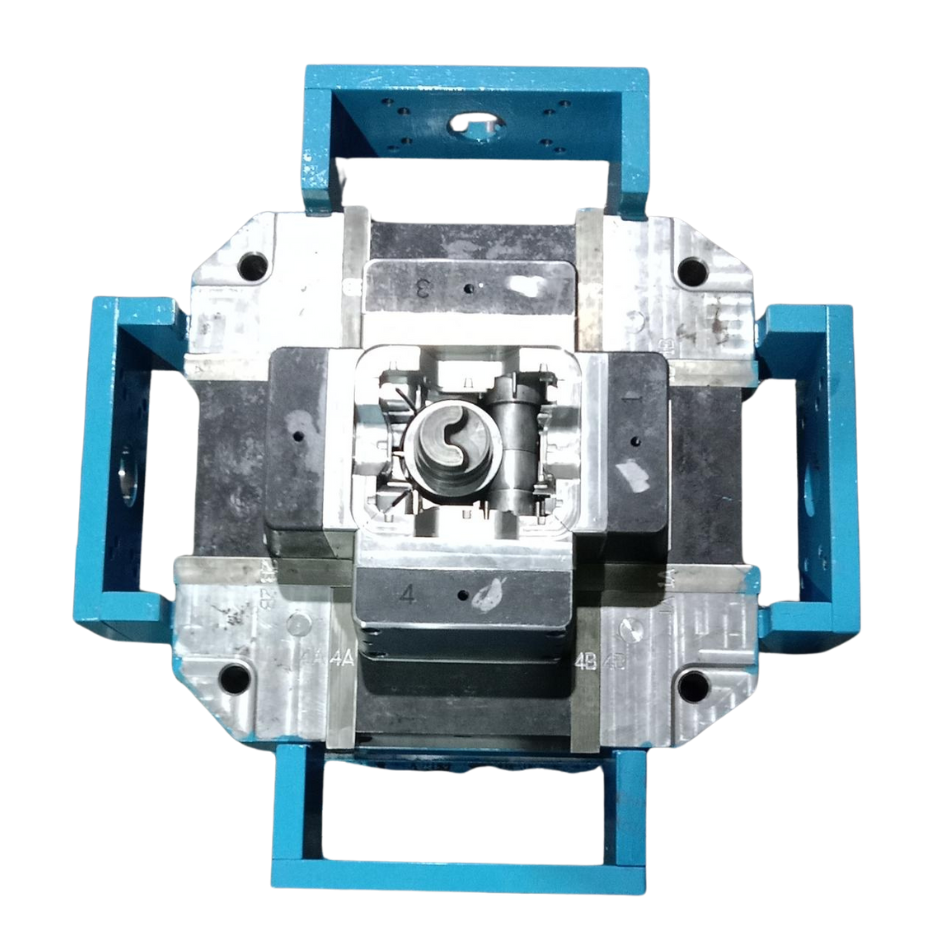
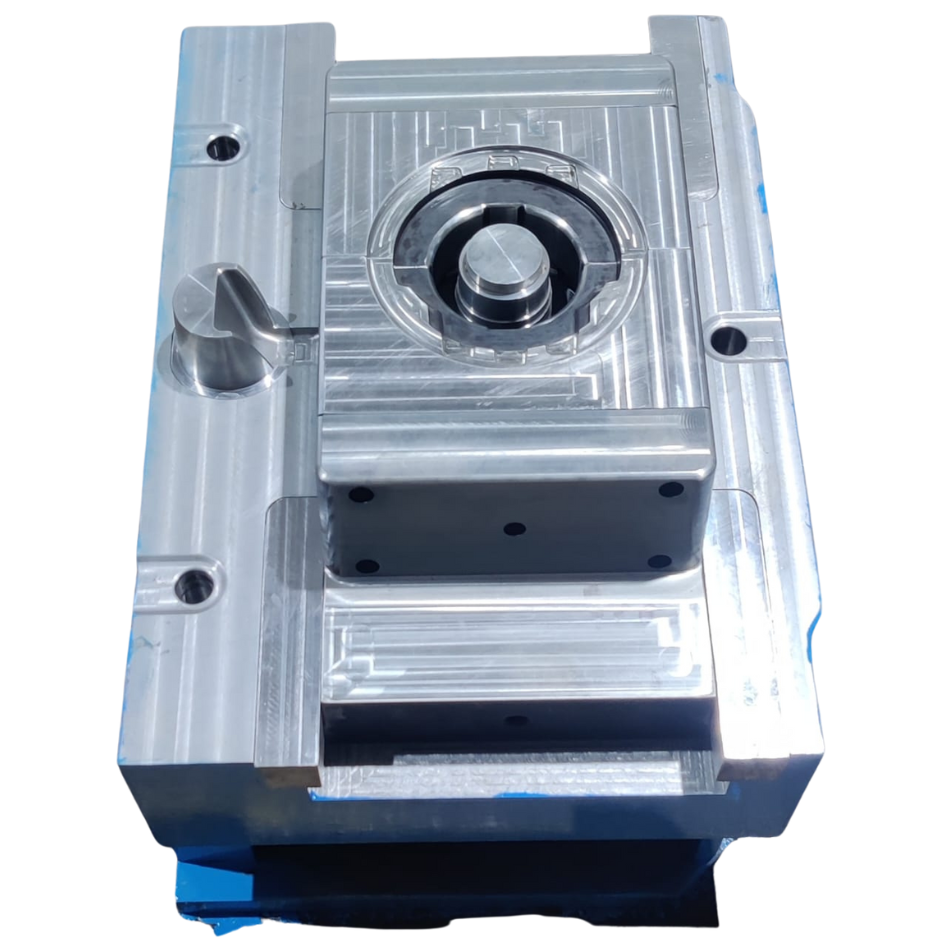
Die Making For Pressure Die Cast
Die Machining for Pressure Die Casting at Vision Metal Cast
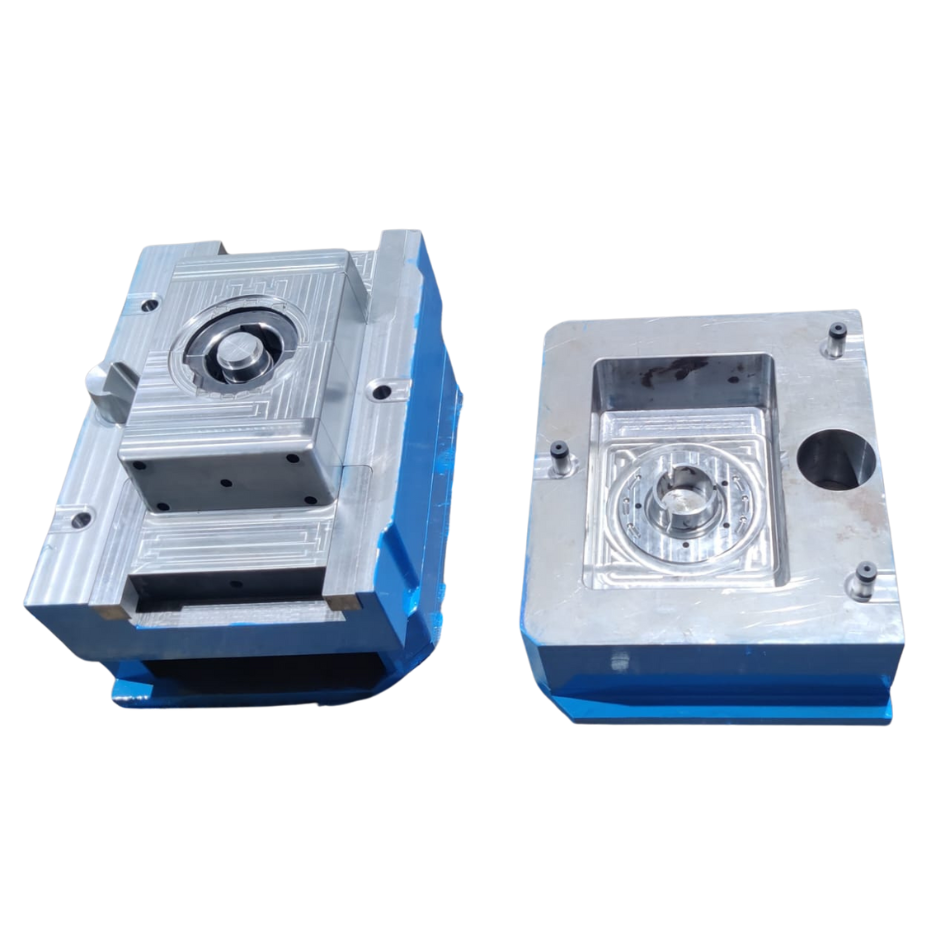
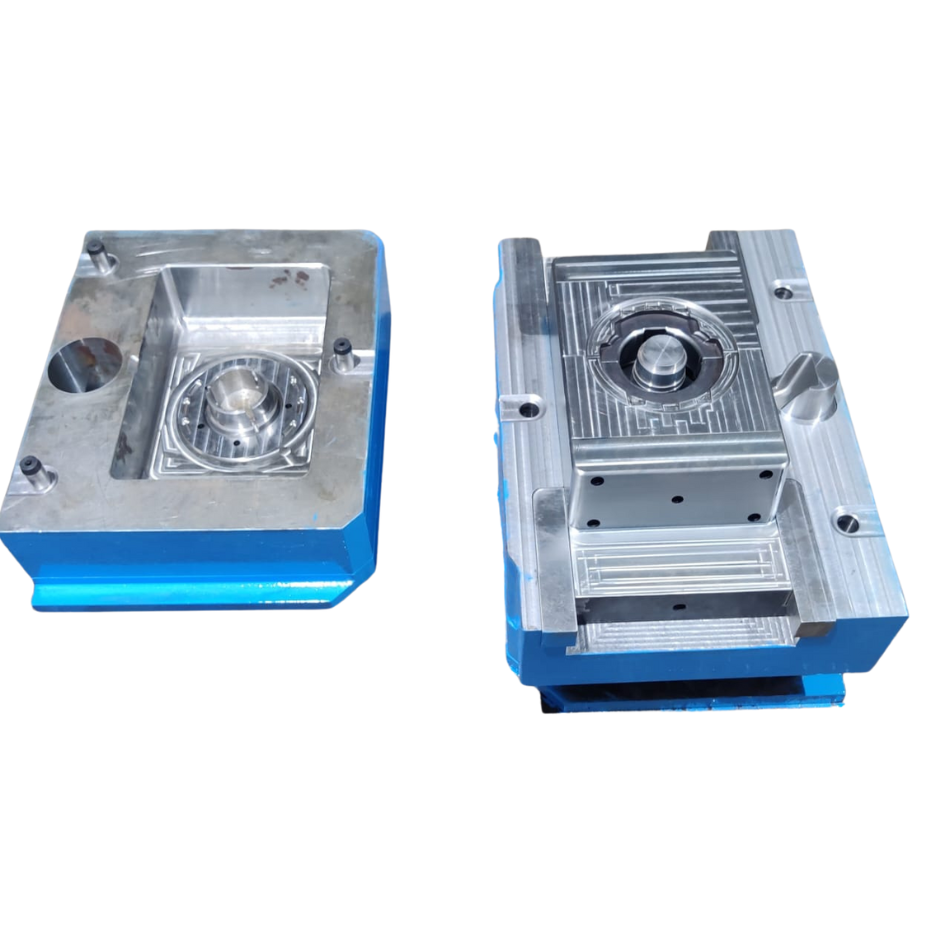
Die machining is an essential part of the pressure die casting process. At Vision Metal Cast, we utilize advanced machining techniques to create highly detailed and accurate molds for our casting operations. The precision machining of dies ensures that they can withstand the high pressure and temperature involved in the casting process, allowing us to produce complex and intricate shapes with tight tolerances.
CNC Milling: For precise shaping and fine detailing.
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): For intricate shapes and hard materials.
Surface Grinding: To achieve smooth and even surfaces for better casting finishes.
Assembly and Testing: Ensuring all components fit perfectly before the casting process.
Why Choose Pressure Die Casting?
High Precision & Complex Shapes – Achieve intricate details with superior accuracy.
Efficiency & Cost-Effectiveness – Mass production with minimal material waste.
Excellent Surface Finish – Requires minimal post-processing.
Superior Strength & Durability – Ideal for demanding industrial applications.
Material Selection and Spectro Testing
Raw Material Selection
We use high-grade aluminum alloys that meet industry standards for strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
The aluminum ingots are inspected before melting to ensure they are free from impurities and defects.
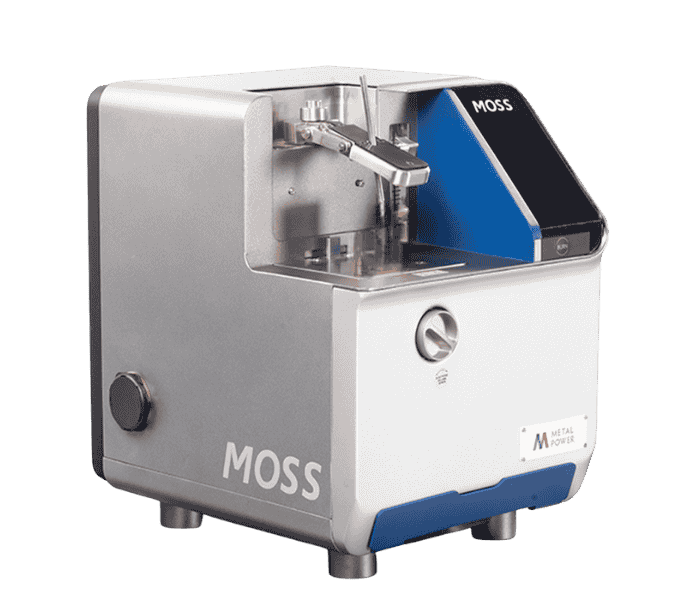
Spectro Testing with Moose Machine
Before casting, we conduct a spectrometric analysis using a Moose Machine to verify the chemical composition of the aluminum alloy.
This testing ensures that the alloy meets required specifications for elements like Si, Mg, Fe, Cu, Zn, Ti, Mn, and Al.
This process helps in maintaining consistent mechanical properties and ensuring high-quality finished products.
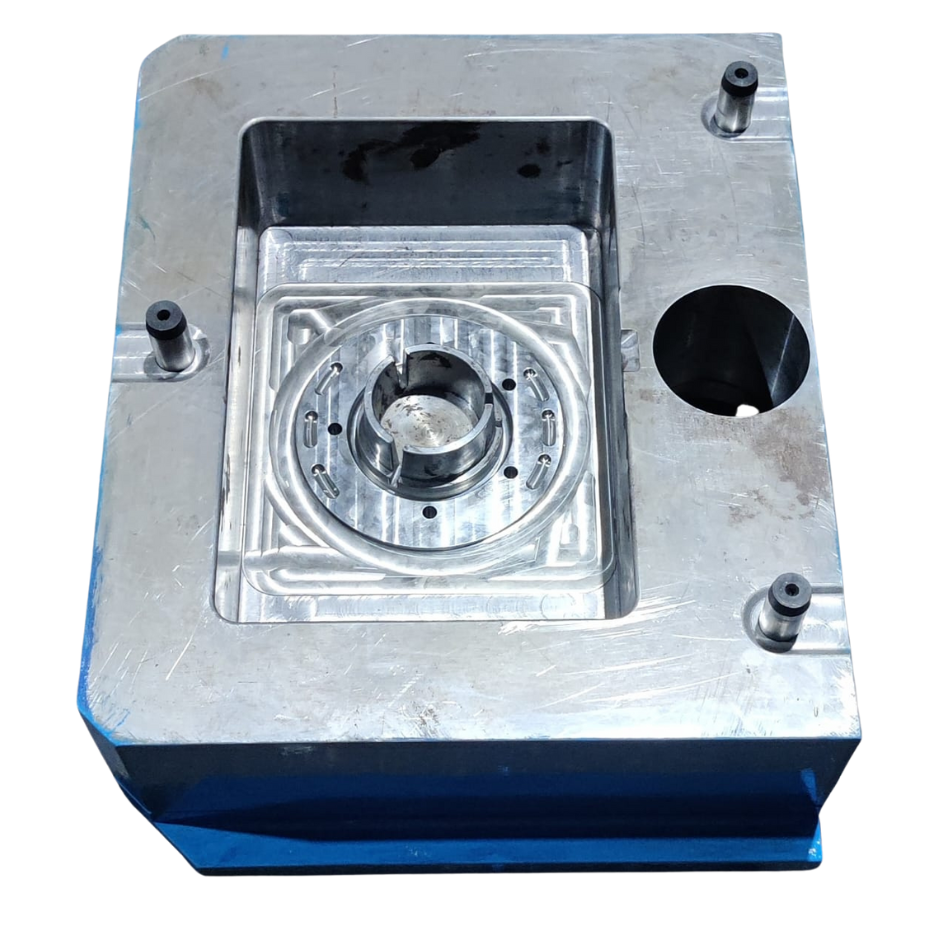
Die Making Process for Pressure Die Casting (SME Process)
Die Design & Engineering
The die is designed using CAD software (SolidWorks, AutoCAD, or Pro-E) to ensure precision and durability.
Thermal simulations are conducted to analyze heat distribution and cooling requirements.
Flow analysis is performed to optimize metal flow and minimize defects such as porosity and shrinkage.
Selection of Die Material
H13 Tool Steel is commonly used due to its high thermal resistance and durability.
Other high-quality tool steels such as H11, SKD61, and 1.2344 are considered based on the casting volume and complexity.
The die steel is inspected for hardness, grain structure, and resistance to thermal fatigue.
Machining & Fabrication
CNC Milling & EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) are used to achieve high precision in cavity and core design.
Grinding and polishing ensure a smooth surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Hardening & Tempering processes improve the die’s wear resistance and lifespan.
Assembly & Testing
The die components (core, cavity, ejector pins, runner systems) are assembled and aligned with tight tolerances.
Trial Casting Runs are conducted to validate the performance of the die before mass production.
Any defects in the initial runs are analyzed, and corrections are made through re-machining or surface treatments.
Die Maintenance & Life Cycle Management
Regular die inspection and maintenance are performed to prevent premature wear and failure.
Surface Coatings (Nitriding, PVD, and CVD coatings) are applied to extend die life.
Cooling channel maintenance ensures efficient heat dissipation and prevents thermal fatigue.
Melting and Degassing
Melting
The aluminum is melted in an external furnace at approximately 680–750°C.
Temperature control is crucial to avoid excessive oxidation and gas absorption.
Degassing & Fluxing
Degassing: We use inert gases (argon or nitrogen) to remove dissolved hydrogen, which can cause porosity in the final casting.
Fluxing: Specialized fluxes are added to remove oxides and other impurities to maintain metal purity.
Cold Chamber Die Casting Process
Metal Transfer to Shot Sleeve
The molten aluminum is poured into the cold chamber shot sleeve using an automated ladle or manually, depending on the job size.
Injection into Mold Cavity
A high-pressure hydraulic piston forces the molten aluminum into the steel mold at high speed and pressure.
The pressure ensures that the metal fills all intricate mold details and minimizes shrinkage defects.
Solidification & Ejection
Once the aluminum solidifies in the mold, the die halves separate, and the casting is ejected using ejector pins.
The cooling time is optimized based on part thickness and mold temperature control.
Post-Casting Operations
Trimming & Deburring
Excess material from casting (flash, runners, and sprues) is removed using trimming presses and manual grinding tools.
Heat Treatment (If Required)
Certain components undergo T6 heat treatment to enhance their mechanical properties like strength and hardness.
Surface Finishing
Shot Blasting: Removes surface imperfections and provides a uniform matte finish.
Machining: CNC machining is used for precise finishing and achieving tight tolerances.
Coating & Painting: If required, components are coated with powder coating or anodizing for better corrosion resistance.
Quality Control & Inspection
Visual & Dimensional Inspection
Every casting is visually inspected for defects like porosity, cracks, and surface irregularities.
Dimensional accuracy is checked using CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine), Vernier calipers, and micrometers.
Pressure Leak Testing (If Required)
Components used for hydraulic and pneumatic applications undergo pressure leak testing to ensure no leakage under operating conditions.
Spectro Re-Verification
Final products are rechecked using Moose Machine spectro analysis to ensure chemical consistency.
Packaging & Dispatch
Degreasing & Cleaning
Each component is thoroughly degreased to remove any residual oil, dust, or contaminants from the manufacturing process.
If necessary, components undergo ultrasonic cleaning for superior cleanliness.
Packing Methods
Parts are packed based on size, weight, and customer requirements:
Small components: Packed in anti-static plastic bags or shrink wrap.
Medium-sized components: Wrapped in bubble wrap or foam sheets and placed in reinforced cardboard boxes.
Large components: Placed in wooden crates or metal containers for safe transit.